Products Description
Machines for sorting waste are a system engineering project integrating mechanical, automated, and intelligent identification technologies. Its core objective is to separate different components in mixed household waste—such as plastics, paper, metals, and organic matter—through a series of physical methods, laying the foundation for subsequent recycling and reuse.
The entire production line typically follows a process of “pre-treatment → core sorting → back-end processing,” achieving automated and continuous operation.
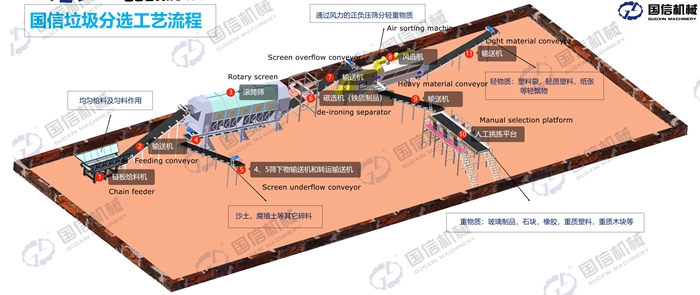
Working Principle of Machines for Sorting Waste:
I: Uniform Feeding and Bag-Breaking Pre-treatment
1. Feeding and Conveying:
After the garbage truck unloads the mixed waste into the unloading hopper, it is uniformly and controllably conveyed to the production line by a plate feeder or chain conveyor. This step ensures the stability and continuity of subsequent processes.
2. Bag Breaking and Coarse Crushing:
Bagged waste is the main obstacle to sorting. The bag-breaking machine quickly tears open the garbage bags through the shearing action of a rotating cutter shaft, fully exposing the materials inside. Subsequently, the coarse crusher will initially pulverize large pieces of waste, making them uniform in size for easier subsequent screening.
II: Multi-stage Screening and Core Sorting
This is the “essence” of the entire sorting process, achieving fine separation through various technologies.
3. Screening (Sorting by Size):
Trommel Screen: This is the key screening equipment. Material enters the slowly rotating trommel screen and is separated into components of different particle sizes according to different apertures. Typically, small-sized organic matter, soil, glass fragments, etc., are screened out; medium-sized mixtures (such as plastics and paper) proceed to the next stage; large debris is separated.
Vibrating Screen: Used for further grading of the undersize material, improving the purity of the material.
4. Magnetic Separation (Recovering Ferrous Metals):
The screened material passes through a magnetic separator. Its powerful magnetic force can automatically attract and separate ferrous metals (such as canned goods and sheet metal), achieving the recovery of high-value metals.
5. Air Separation (Sorting by Weight and Density):
Eddy Current Separator: Used for recycling non-ferrous metals (such as aluminum cans and copper parts). This equipment uses a high-speed alternating magnetic field to generate eddy currents inside the non-ferrous metals, creating a repulsive force that “ejects” them from the mixture, resulting in extremely high sorting accuracy.
Air Separator: Utilizes controlled airflow to separate lightweight materials (such as plastic film and paper) from heavy materials (such as hard plastics and stones). This is a highly efficient and low-cost density-based sorting method.
6. Intelligent Photoelectric Separation (Sorting by Material and Color):
This is the “smart brain” of modern sorting lines. Photoelectric separators utilize near-infrared (NIR) sensors to illuminate materials, allowing different substances to reflect unique “spectral fingerprints.” By identifying these spectra, the system can accurately distinguish between various plastic types, such as PET, HDPE, and PP, as well as differentiate between paper and cardboard. The target material is precisely blown out through high-pressure airflow nozzles.
III. Resource Recovery and Packaging
7. Crushing and Washing:
The sorted pure plastics, paper, and other materials enter a fine shredder to be pulverized into flakes or granules. They then enter a washing line where, through friction and rinsing processes, stains and labels are removed.
8. Compression and Baling:
The cleaned plastic flakes, sorted paper products, metals, etc., are finally fed into a hydraulic baler, where they are compressed into high-density, well-formed brick-shaped bales. This significantly reduces volume, facilitating transportation and storage, and allowing them to be sold as high-quality recycled raw materials to downstream companies.
A modern waste sorting production line, through the integration of multiple technologies including trommel screening, magnetic separation, air separation, and photoelectric separation, can achieve a sorting purity of over 95%, truly turning waste into a resource.
We provide one-stop services from planning and design, equipment manufacturing, installation and commissioning, to operation and maintenance. We are committed to using reliable machinery and advanced technology to create efficient, energy-saving, and profitable waste resource recovery solutions for global clients, jointly promoting the development of the circular economy.


